5 must-ask questions for evaluating new product opportunities:
1. Who is the customer? (Segment) 2. How do we know their problems? (Discovery) 3. How do we reach out to them? (Go To Market) 4. How do we iterate/ scale? (Roadmap) 5. How do we know we are succeeding? (Metrics)Saturday, August 6, 2022
Sunday, May 29, 2022
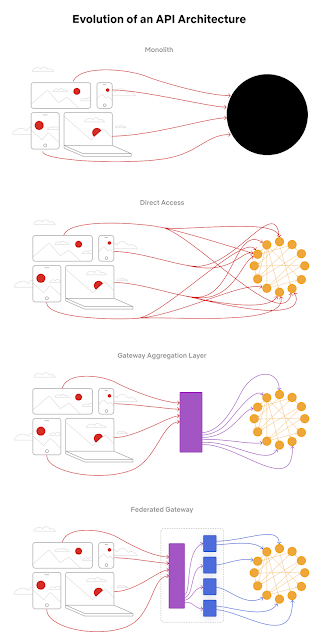
Evolution of the Netflix API architecture
Monolith. The application is packaged and deployed as a monolith, such as a single Java WAR file, Rails app, etc. Most startups begin with a monolith architecture.
Direct access. In this architecture, a client app can make requests directly to the microservices. With hundreds or even thousands of microservices, exposing all of them to clients is not ideal.
Gateway aggregation layer. Some use cases may span multiple services, we need a gateway aggregation layer. Imagine the Netflix app needs 3 APIs (movie, production, talent) to render the frontend. The gateway aggregation layer makes it possible.
Federated gateway. As the number of developers grew and domain complexity increased, developing the API aggregation layer became increasingly harder. GraphQL federation allows Netflix to set up a single GraphQL gateway that fetches data from all the other APIs.
References:
[1] How Netflix Scales its API with GraphQL Federation (Part 1): https://netflixtechblog.com/
[2] Why You Can't Talk About Microservices Without Mentioning Netflix: https://smartbear.com/blog/
Tuesday, May 24, 2022
How to Scale website? Its also applicable to all the products
Suppose we have two services: inventory service (handles product descriptions and inventory management) and user service (handles user information, registration, login, etc.).
Step 1 - With the growth of the user base, one single application server cannot handle the traffic anymore. We put the application server and the database server into two separate servers.
Step 2 - The business continues to grow, and a single application server is no longer enough. So we deploy a cluster of application servers.
Step 3 - Now the incoming requests have to be routed to multiple application servers, how can we ensure each application server gets an even load? The load balancer handles this nicely.
Sunday, May 22, 2022
How does CDC (Change Data Capture) work?
Data stored in the database could be interesting to many other data systems, such as analytics, AI, etc. If we have thousands of data systems, do we have to write thousands of converters?
The answer is NO. Change data capture (CDC) is a process that can solve the problem. This is how CDC works:
1. Data is written to the database normally.
2. Database uses the transaction log to record the modifications.
3. CDC software uses the source connector to connect to the database and reads the transaction log.
4. The source connector publishes the log to the message queue.
5. CDC software uses its sink connector to consume the log.
6. The sink connector writes the log content to the destination.
All these operations except step 1 are transparent to the user. Popular CDC solutions, such as Debezium, have connectors for most databases, such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, DB2, Oracle, etc. We only need to set up the CDC link between two databases and the data will automatically flow to the destination.
Saturday, May 21, 2022
How to design Secure Web API?
𝐓𝐨𝐤𝐞𝐧 𝐛𝐚𝐬𝐞𝐝
Step 1 - the user enters their password into the client, and the client sends the password to the Authentication Server.
Step 2 - the Authentication Server authenticates the credentials and generates a token with an expiry time.
Steps 3 and 4 - now the client can send requests to access server resources with the token in the HTTP header. This access is valid until the token expires.
𝐇𝐌𝐀𝐂 𝐛𝐚𝐬𝐞𝐝
This mechanism generates a Message Authentication Code (signature) by using a hash function (SHA256 or MD5).
Steps 1 and 2 - the server generates two keys, one is Public APP ID (public key) and the other one is API Key (private key).
Step 3 - we now generate a HMAC signature on the client side (hmac A). This signature is generated with a set of attributes listed in the diagram.
Step 4 - the client sends requests to access server resources with hmac A in the HTTP header.
Step 5 - the server receives the request which contains the request data and the authentication header. It extracts the necessary attributes from the request and uses the API key that’s stored on the server side to generate a signature (hmac B.)
Steps 6 and 7 - the server compares hmac A (generated on the client side) and hmac B (generated on the server side). If they are matched, the requested resource will be returned to the client.
Question - How does HMAC authentication ensure data integrity
Why do we include “request timestamp” in HMAC signature generation?
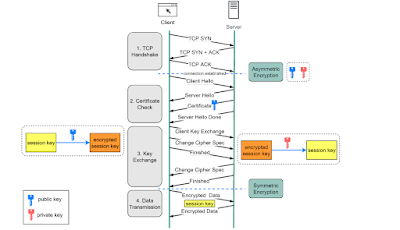
How does HTTPS work?
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is an extension of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP.) HTTPS transmits encrypted data using Transport Layer Security (TLS.) If the data is hijacked online, all the hijacker gets is binary code.
Monday, May 16, 2022
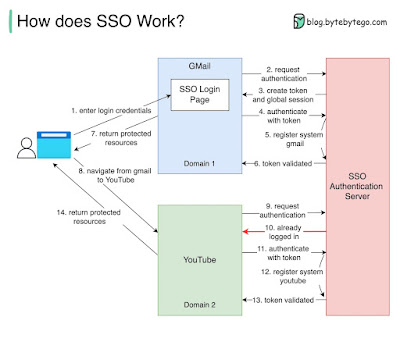
How does SSO Work - Thanks to bytebytego.com
Step 1: A user visits Gmail, or any email service. Gmail finds the user is not logged in and so redirects them to the SSO authentication server, which also finds the user is not logged in. As a result, the user is redirected to the SSO login page, where they enter their login credentials.
Steps 2-3: The SSO authentication server validates the credentials, creates the global session for the user, and creates a token.
Steps 4-7: Gmail validates the token in the SSO authentication server. The authentication server registers the Gmail system, and returns “valid.” Gmail returns the protected resource to the user.
Step 8: From Gmail, the user navigates to another Google-owned website, for example, YouTube.
Steps 9-10: YouTube finds the user is not logged in, and then requests authentication. The SSO authentication server finds the user is already logged in and returns the token.
Step 11-14: YouTube validates the token in the SSO authentication server. The authentication server registers the YouTube system, and returns “valid.” YouTube returns the protected resource to the user.
The process is complete and the user gets back access to their account.